
Minimally invasive bunion surgery (MIBS) is an approach to correcting bunion problems that’s appealing because it involves fewer risks and less downtime.
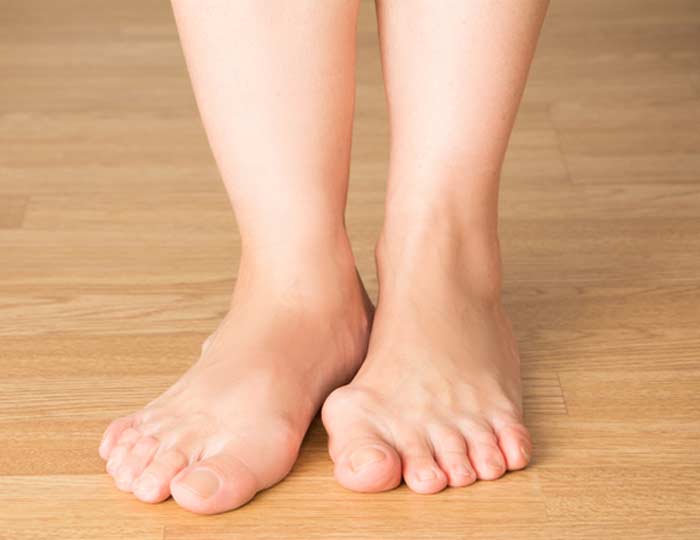
A bunion is a common foot condition characterized by a protruding bump on the outside portion of the part of the joint that links the big toe to the rest of the foot. It can become a problematic and painful deformity when the big toe turns inward as the bony bump becomes larger or more misaligned.
If conservative treatments that may include medication and the use of padding, shoe inserts, and similar bunion-related products aren’t effective, surgery may be recommended.
What Is Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery?
MIBS simply refers to techniques performed during bunion surgery in a way that reduces incision size and trauma to the affected part of the foot. Typically, less invasive methods are used during procedures that release tension in ligaments and soft tissues to relieve pressure on adjacent toes, although other bunion-related procedures can be informed with minimally invasive methods under the right circumstances. MIBS usually involves:
- Very small (2-3 mm) incisions
- A slender, lighted tube with an attached lens that provides a view of the affected area
- Use of a live X-ray (fluoroscopy) to help with surgical instrument guidance

How Does It Differ from Traditional Surgery?
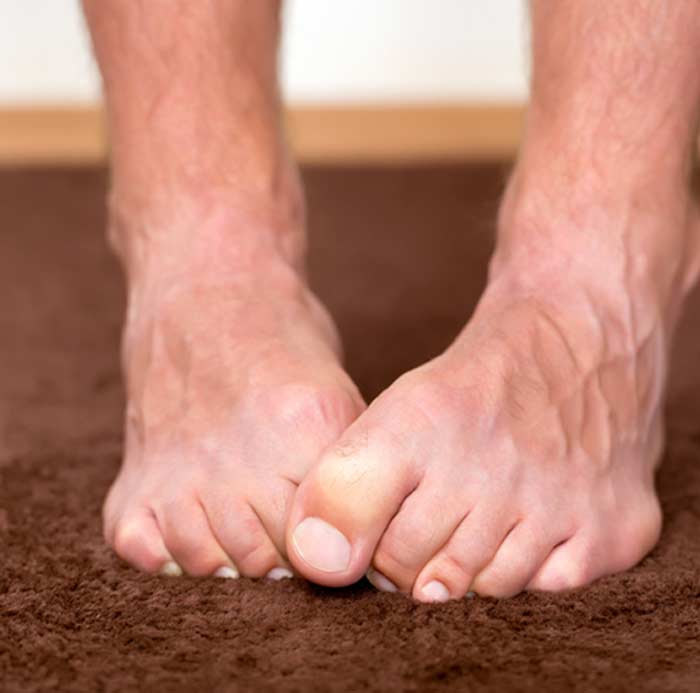
During tradition bunion surgery, a larger incision is made to reach bones, tendons, and ligaments in the affected area. With MIBS, smaller incisions are made. With some procedures, only one or two small cuts may be necessary. MIBS is also usually performed without general anesthesia. Instead, a local block is used to numb the affected area. Traditional surgery for bunions sometimes requires internal hardware that may include screws, plates, and wires. With MIBS, small fractures are often made to realign the bones. This means there’s no need for hardware.
Who Are Ideal Candidates for MIBS?
Whether or not MIBS is an option will depend on the extent of the deformity. For instance, if parts of bones need to be removed to restore proper alignment, traditional surgery may be the better option. If a bunion can be corrected with small cuts to bones and tissues (osteotomy), it’s often possible to use less-invasive techniques. Also, minimally invasive techniques are sometimes used to remove parts of the damaged joint (resection arthroplasty) so the metatarsals can be realigned.
In some cases, minimally invasive arthroscopic techniques can be used to remove the bony growth that forms the visible part of the bunion (exostectomy). Typically, preferred candidates for MIBS are patients without significant underlying health issues or related deformities like hammertoe that may require more extensive surgery.
What Are Benefits Associated with Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery?
Other than smaller incisions, minimally invasive bunion surgery is often preferred because it’s usually done as an outpatient procedure. In fact, it’s not unusual for patients to walk out after their surgery and return to most of their normal activities – except for anything involving significant foot pressure. Additional benefits associated with MIBS include:
- Minimal tissue damage
- Less post-procedure pain
- Faster recovery
- Fewer stitches and less scarring
- Reduced infection risk
Bunions are technically a subluxating (incomplete or partially dislocated) big toe joint and not excess bone growth. Therefore, it’s possible for this abnormality to occur again after minimally invasive bunion surgery is performed. This risk can be minimized by ensuring that the right procedure is recommended to correct a patient’s bunion-related deformity. It’s just as important to wear supportive footwear after surgery to prevent other foot problems from developing.
