
Anyone who thinks they may have torn a ligament should see a doctor right away.
Ligaments connect bones together. They are present in the joints to provide a passive limitation to how much the bones can move, and are a type of fibrous tissue that is tough.
Injuries to ligaments are not uncommon, and ligament tears are something all patients should be aware of.
Causes
This injury can occur in any joint. However, ligament tears are most common in the ankles and knees. This is because these joints are under high stress due to being weight-bearing. The tears happen when a ligament is stretched beyond its normal range. Landing awkwardly and abnormal twisting can cause this stretching to result in a tear.
Certain factors may increase someone’s risk of a ligament tear. These include:
- Exercising on a surface that is slippery or uneven
- Exercising with tired muscles
- Not warming up sufficiently before significant activity
- Using poor equipment or wearing shoes that do not fit well
- Weak muscles and poor conditioning

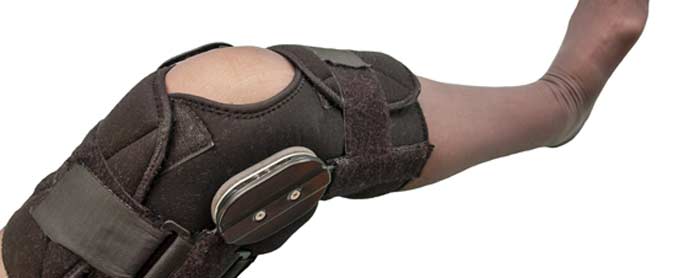
Symptoms
When a ligament is torn, the pain can come on suddenly. It can be severe in many cases. Significant swelling is not uncommon. The joint can become unstable. When the torn ligament is in the leg, it can make it hard for someone to bear weight and walk. It is also possible to lose some range of motion and experience bruising where the torn ligament is located.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves determining if a ligament tear is present and the grade of the tear. The grades include:
- Grade 1: This is a minor tear that typically heals without extensive medical intervention.
- Grade 2: This tear is more disabling and significant. It might require that the patient avoid putting weight on the affected joint for a short time. It may take up to 12 weeks for complete healing.
- Grade 3: This is a complete tearing of a ligament. Seeing an orthopedic specialist is typically recommended since this tear might require surgery.
The doctor will visually inspect the affected joint to look for signs of a ligament tear. They will ask about the patient’s pain and symptoms. To get a better look at the joint structure, imaging tests might be performed. This could include some general X-rays to look at the bones, or a CT scan or MRI to visualize the tissues.
Treatment
Medications are commonly used to control the inflammation and pain associated with a ligament tear. For tears that are mild, over-the-counter medications are typically recommended. For more severe injuries, the doctor may prescribe a short-term narcotic medicine.
For severe tears, surgery might be needed to repair it. The exact technique will depend on the affected ligament and the extent of the injury. Physical therapy may be used for mild to moderate tears. It is also often used after surgery to strengthen the affected joint.
