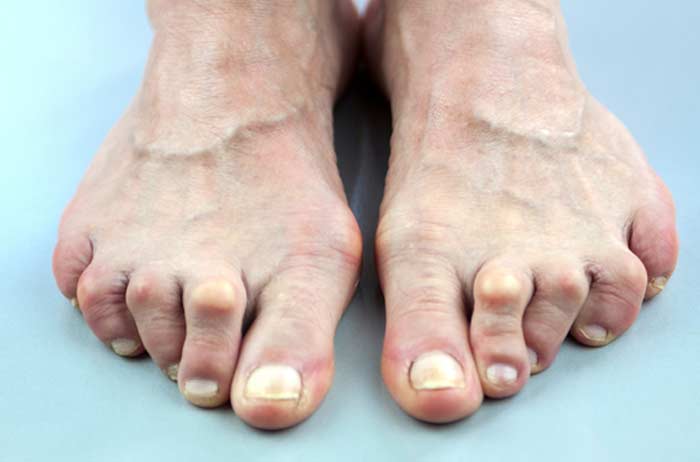
There are more than a hundred forms of arthritis, with the most common types being osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Affecting more than 300 million people worldwide, arthritis is an inflammation-based condition that often causes issues with multiple joints by triggering tissue swelling and facilitating the breakdown of the cartilage that protects the ends of bones.
There is no cure for arthritis, however, there are ways to manage pain and ease discomfort from related symptoms that sometimes have a serious impact on quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms
Not all joint-related aches and pains are due to arthritis. It’s also possible for joints to be affected by problems related to stress fractures, muscle strains, bursitis, or dislocations. Signs and symptoms associated with common types of arthritis include:
- Recurring pain around certain joints
- Noticeable swelling, redness, or tenderness
- Discomfort that becomes worse with specific movements
- Decreased range of motion or flexibility
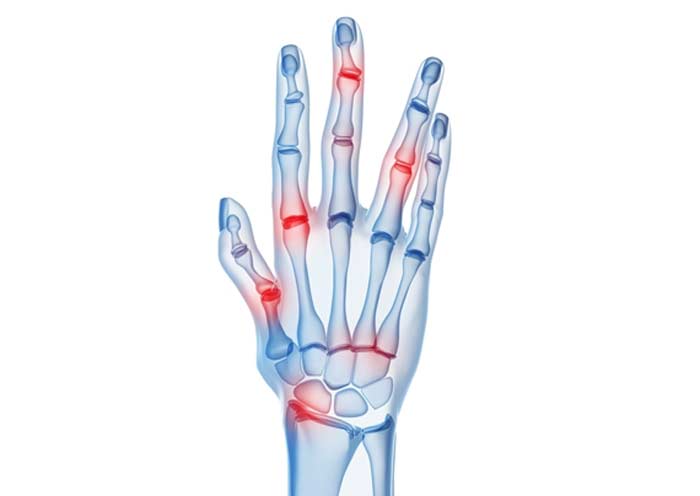

Examination and Diagnosis
The first step in treating or managing arthritis symptoms is to perform a thorough examination and make a positive diagnosis. This process allows the correct form of arthritis to be treated and the extent of damage to affected joints and tissues to be assessed. In addition to X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, diagnosis may also involve:
- Blood and urine testing
- Collection of joint fluid with a needle in the joint space (aspiration)
- Ultrasound to assess bone density
Treatment with Medication
Discomfort experienced during the early stages of arthritis is often managed with medication. Analgesics like acetaminophen, tramadol, and hydrocodone may help with pain. Both over-the-counter and prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often recommended to reduce inflammation around joints. Some patients also benefit from biologic response modifiers that target protein molecules in the immune system and corticosteroids in oral or injectable form.
Physical Therapy for Arthritis
Another common way to treat various forms of arthritis is with physical therapy. What’s good about PT is the many techniques that can be recommended for arthritis sufferers. Braces or splints may be used under certain circumstances, although it’s more likely that some type of exercise program will be suggested. Pelvic tilts, planking, ball exercises, and other core-strengthening exercises, for example, may improve range of motion and ease pressure on joints by improving the stability and strength of joint-supporting muscle groups. Types of physical therapy that may minimize arthritis pain also include:
- Massage therapy
- Aqua (water-based) therapies
- Hot and cold applications
Lifestyle Adjustments
Symptoms related to arthritis are sometimes manageable with lifestyle adjustments, especially with diet and exercise habits. Losing weight can reduce stress on joints, while getting more productive sleep may give tissues and joints more time to naturally heal. With diet, avoiding sugary snacks and other foods linked to inflammation may improve results with other arthritis treatments. Green, leafy vegetables, bright-colored fruits, berries, walnuts and almonds, and salmon, mackerel, and other fatty fish are among the foods that may naturally fight inflammation for people living with arthritis.
Surgery is rarely the first attempt at treating any form of arthritis since it’s a progressive condition. It’s when joints and supporting muscles, ligaments, and tendons have been severely damaged that surgery that might include joint repair, fusion, or replacement may become an option. Surgery does not prevent arthritis from affecting a repaired joint again. What it may do, however, is restore the function of joints that provide essential support for daily movements by improving strength, flexibility, stability, and range of motion.
